Covid-19 left everyone stranded in the year 2020, in terms of being able to avail health facilities and many other things. Overwhelmed healthcare facilities and lesser access to in-person consultation sessions significantly accelerated the need for remote medical care. Other than healthcare professionals, the tech industry has also been trying immensely hard to help the healthcare facilities get life back to normal.
IoT, which is defined as the synchronization of several machines, devices, and appliances linked to the internet through multiple networks, helps with remote diagnostics, treatment, and monitoring. This technology can bring advancement to patient care by connecting patients to health practitioners, and aiding the collection and study of data that can advance patient care.
In times of social distancing, IoT has proved its worth very well by enabling the diagnosis and treatment of patients remotely and facilitating the delivery of vital medicine and medical equipment to isolated areas. Let’s have a look at different uses of IoT technology in remote patient monitoring and care during the pandemic crisis.
IoT for Healthcare Industry: Challenges and Opportunities
IoT arrangement in the healthcare sector often comes with challenges around connectivity, power, spectrum, and bandwidth requirements, as well as price structure. However, the concentrated cost of computing (including sensors) and augmented mobile broadband penetration are likely to drive the use of IoT in the healthcare industry. The economical price structure of standardised low-power wireless technologies will also help that trend.
The IoT technology offers evolving markets an opportunity to fight COVID-19 resourcefully. It also helps in plugging critical gaps in affordability, worth, and access. Other than COVID-19, added development of IoT could help foresee future pandemics, by using statistical-based devices and converging with artificial intelligence (AI), and big data. All this could make IoT a key enabler of healthcare transformation soon.
Increased implementation of smart badges with contactless interfaces
A contactless smart card/badge comprises a chip and a radio frequency identification (RFID) antenna which is connected to the chip for reading and writing information. These contactless cards are not required to be swiped or inserted into a smart card reader in order to complete a transaction. Instead, these are only needed to be waved within the electromagnetic field range of the reader in order to read and store the information saved in the chip. These badges have been increasingly used for physical access control in businesses, government, educational, and healthcare institutions to limit physical access to their offices or different areas within a campus.
The contactless smart badges offer a simple, secure, and cost-effective solution to the identity management and access control problems during the pandemic. Contactless, safe entry into buildings has now become very common in college campuses. These IDs work efficiently to open doors, too, as a substitute for swiping an entry card. Additionally, these IDs not only help with student identification but also work as a payment mechanism for different kinds of on-campus transactions.
Use of Contact Badges at Workplaces and Hospitals
Talking about the use of contact badges during Covid-19, many offices, factories, and hospitals started using these contacts to track the virus by adding sensors to their employees’ badges. Some healthcare facilities use it to monitor whether their medical staff members use their hands after their entry and exit from patients’ rooms. On the other hand, some others use it to keep track of expensive assets like IV pumps or wheelchairs, which have a predisposition to go missing.
The system controls the sensors fixed into equipment and location beacons in the rooms at healthcare facilities, which is connected to an online dashboard. Managers or administrators can access this dashboard for multiple uses, such as to checking in or receiving the reports.
When hospitals around the world started reporting that their staff had contracted the virus, industry experts figured they could help the situation. The condition was particularly challenging when hospitals lacked adequate personnel protective equipment. Initial reports stated that at least 880 doctors, nurses, and other medical staff died of the deadly virus.
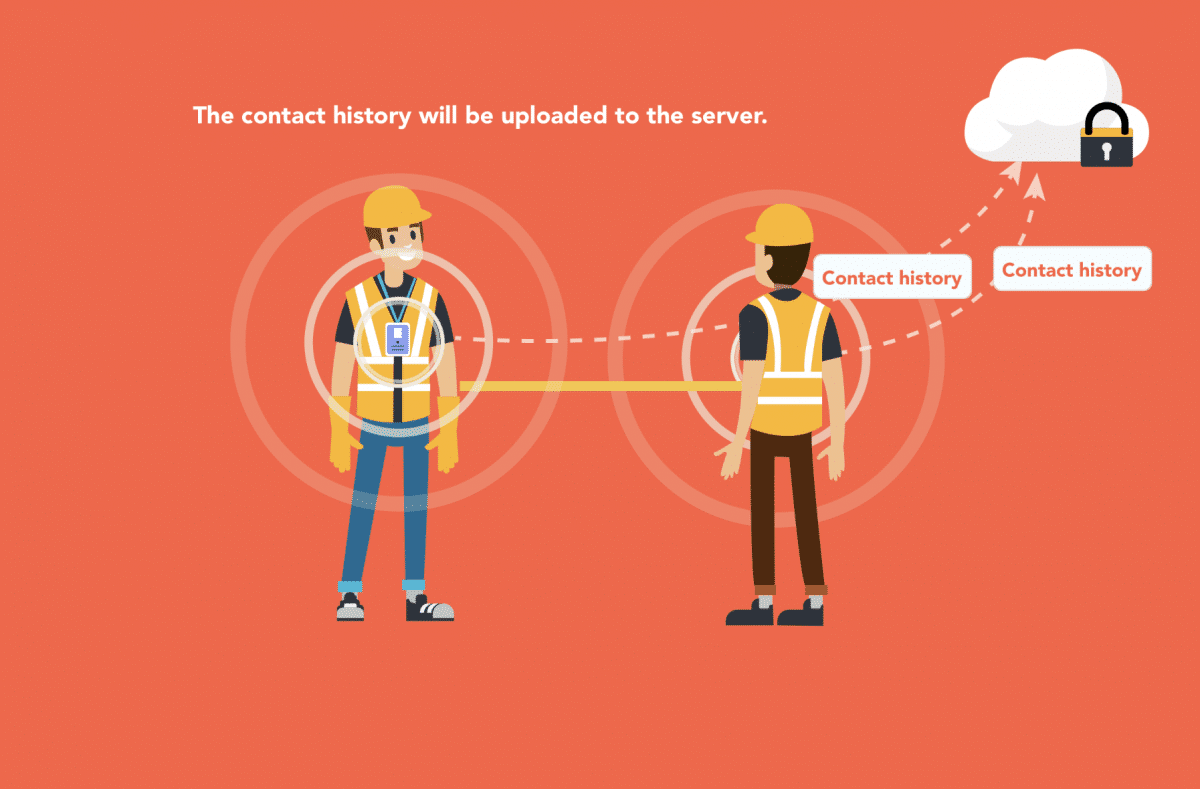
Following such chaos, the IoT experts at Lansitec had the idea of adding sensors to staff badges, which would immensely help in their routine shifts. Their idea was that in case a patient, doctor, nurse, or any other hospital staff member was diagnosed with the Covid-19 virus, they could draw a map with tiny dots, representing people, and the administrators could go back in time to check who might have been close to the person. With this much control, the hospital could take needed steps to quarantine and test them for the virus.
Contact Tracing Badges
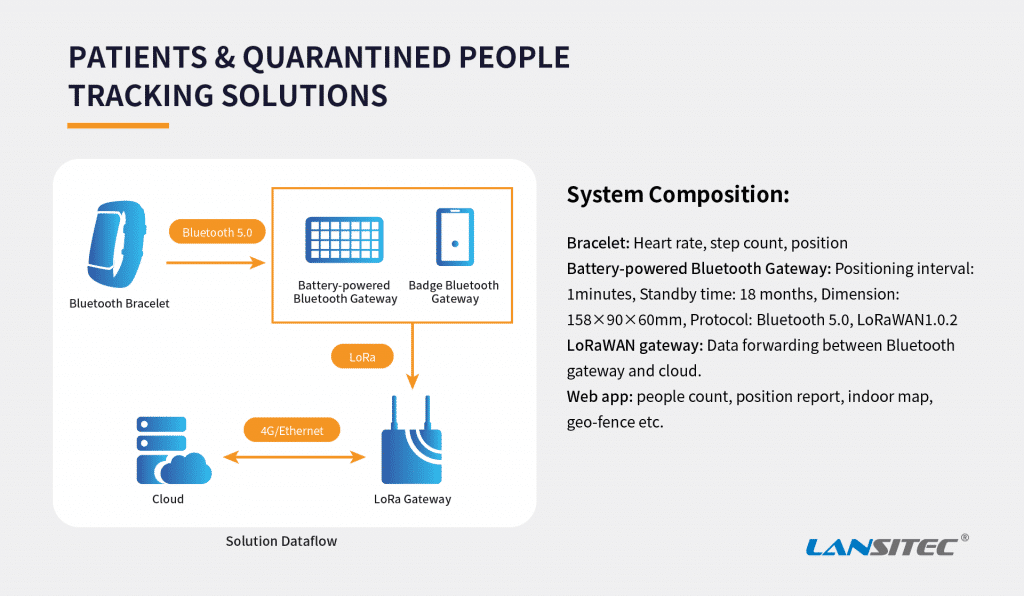
The design of Lansitec contact tracing badges is based on Bluetooth 5.0 and LoRa technology. Since the tracing badges use RSSI for distance calculation and contact tracing, it is primarily used to keep a social distance at the workplace or hospital and is particularly useful during COVID-19.
Proximity detection function: The badge beeps when any other badges approach. An employee or an individual can be alerted by the vibration and sound of the badge without even the LoRa network. Also, if someone is found infected, people who have been closely contacted with him/her can be easily found and isolated. NFC functionality is also integrated into the badge to help proper management.
During the pandemic, it is vital to keep social distance even between co-workers, for people under isolation and protection.
Use cases:
- At power plants and offices: To keep safe distance among workers and specific facilities, and for an overview of personnel
- At automobile plant: Indoor workers tracking with badges, closeness detection, and alert
Functionalities:
- Closeness alert: The badge starts beeping when the distance between two badges is less than 3 meters.
- Contact history: The system has the functionality to keep a record of the time and the location when two or more people have been contacted.
- Geo-fence
- Check-in and check-out tracking along with security check. Easy installation and private network are some additional features.
Considering the high throughput, validation speed, and secure systems, the demand for smart badges is undoubtedly going to rise in the near future, especially in the medical sector and factories.






