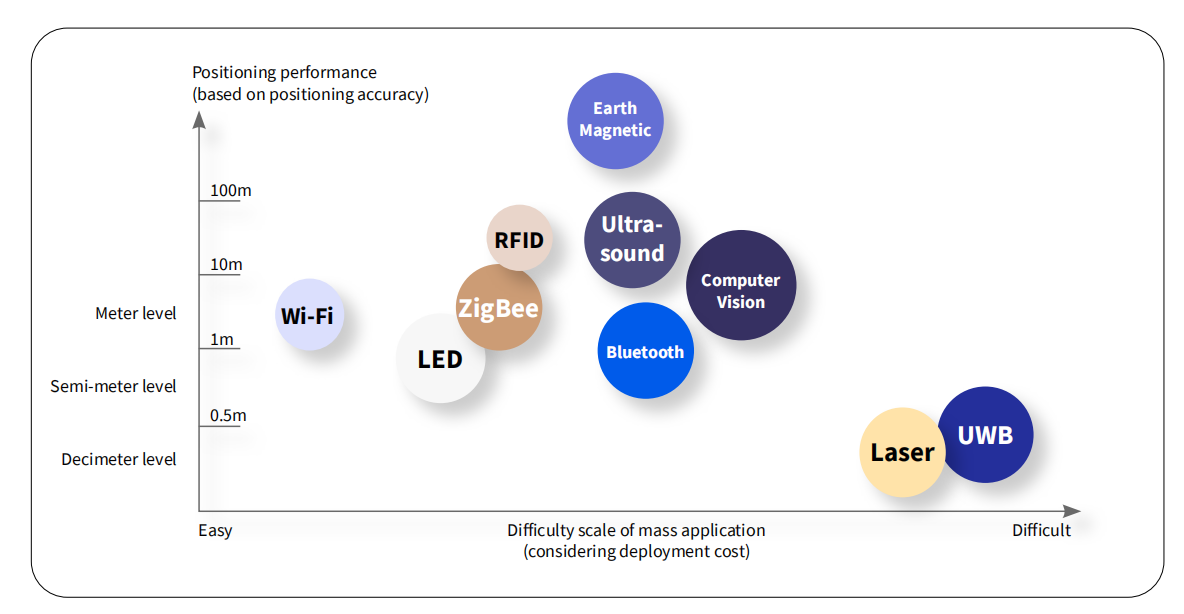
The technologies above are widely used in indoor scenarios. Currently, dozens or even hundreds of technologies exist in this field. Each positioning technology has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, and is suitable in particular application scenarios.
The above diagram compares the positioning performance and deployment difficulty of the mainstream indoor positioning technologies.
Many applications require a combination of fundamental concepts or hybrid technologies. For example, BLE+GNSS+LoRa is used for indoor and outdoor tracking. UWB+BLE is used for accurate positioning and asset management.
When choosing a positioning technology, data transfer method, power supply, and installation method should be taken into consideration. The data transfer methods include ethernet, 4G, 5G, LPWAN (LoRa and NB-IoT). Lansitec has a full range of LPWAN-based Bluetooth gateways, Macro Bluetooth Gateway, Solar Bluetooth Gateway, Compact Bluetooth Gateway, indoor Bluetooth Gateway, NB-IoT Bluetooth Gateway, and other options.
Sensors can also help improve accuracy in specific applications, such as a barometer that can helps to measure the attitude of tracker. The accelerometer can judge the motion state of the tracker to save power on electricity costs.
Explore the Whitepaper: Introduction to the Basic Principles of Positioning Technology








