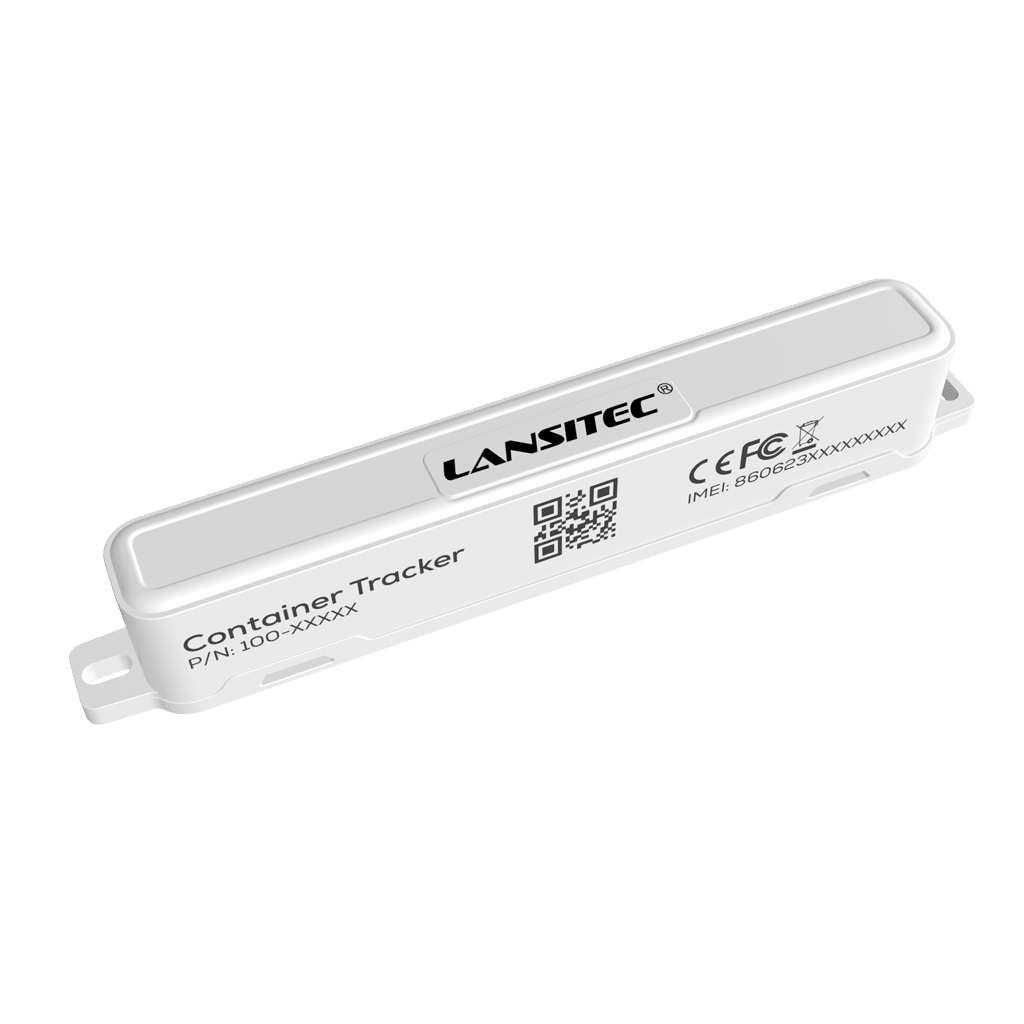
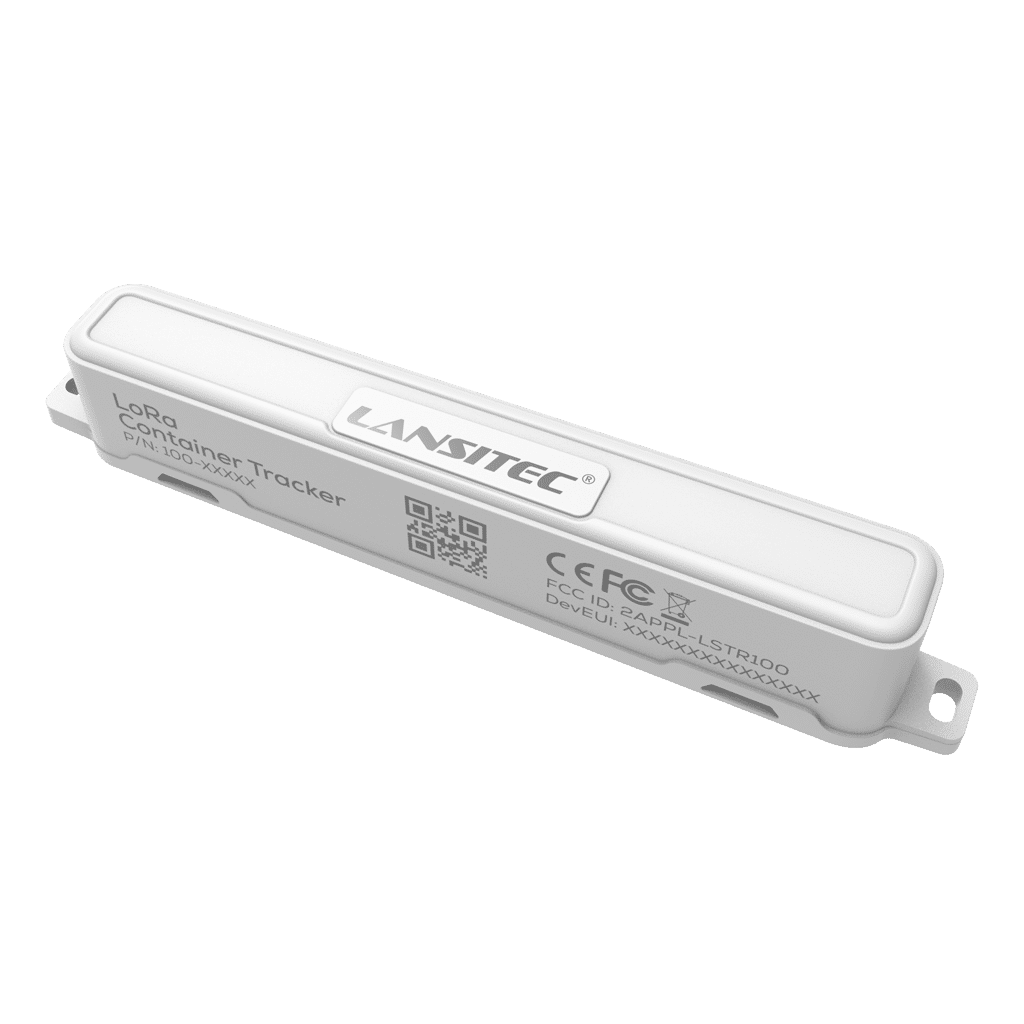
Lansitec Container Tracker Bringing LoRaWAN and NB-IoT in Modern Logistics
Lansitec Container Tracker Bringing LoRaWAN and NB-IoT in Modern Logistics When it comes to logistics and supply chain management, the ability to accurately track containers and assets is not just